plot_variance_comparison_data() creates a connected plot with time as a
categorical variable (i.e. baseline/before and after) on the x-axis and the
variance measure on the y-axis. There are also lines
connecting the "before" data point to the "after" data point for each letter.
Usage
plot_variance_comparison_data(
data,
plot_category,
plot_treatment,
facet_by_sex = "no",
variance_measure = "cv",
baseline_interval = "t0to5",
baseline_label = "Baseline",
post_hormone_interval = "t20to25",
post_hormone_label = "Insulin",
included_sexes = "both",
male_label = "Male",
female_label = "Female",
left_sex = "Female",
test_type,
y_variable_signif_brackets = NULL,
map_signif_level_values = F,
geom_signif_family = "",
geom_signif_text_size = 5,
large_axis_text = "no",
geom_signif_size = 0.4,
mean_line_thickness = 1.2,
mean_point_size = 2.5,
treatment_colour_theme,
theme_options,
save_plot_png = "no",
filename_suffix = "",
ggplot_theme = patchclampplotteR_theme()
)Arguments
- data
A dataframe generated using
make_variance_data().- plot_category
A numeric value specifying the category, which can be used to differentiate different protocol types. In the sample dataset for this package,
plot_category == 2represents experiments where insulin was applied continuously after a 5-minute baseline period.- plot_treatment
A character value specifying the treatment you would like to plot (e.g.
"Control").plot_treatmentrepresents antagonists that were present on the brain slice, or the animals were fasted, etc.- facet_by_sex
A character value (
"yes"or"no") describing if the plots should be faceted by sex. This is only available ifincluded_sexesis"both". The resulting plot will be split in two, with male data on the left and female data on the right.- variance_measure
A character value ("cv" or "VMR"). The variance measures can be either the inverse coefficient of variation squared (
variance_measure == "cv") or variance-to-mean ratio (variance_measure == "VMR").- baseline_interval
A character value indicating the name of the interval used as the baseline. Defaults to
"t0to5", but can be changed. Make sure that this matches the baseline interval that you set inmake_normalized_EPSC_data().- baseline_label
A character value for the x-axis label applied to the pre-hormone state. Defaults to
"Baseline".- post_hormone_interval
A character value specifying the interval used for the data points after a hormone or protocol was applied. This must match the
post_hormone_intervalused inmake_variance_data().- post_hormone_label
A character value for x-axis label applied to the post-hormone or post-protocol state. Defaults to
"Post-hormone"but you will likely change this to the hormone or protocol name.- included_sexes
A character value (
"both","male"or"female"). Useful if you want to have a plot with data from one sex only. Defaults to"both". If you choose a single sex, the resulting plot will have"-males-only"or"-females-only"in the file name.- male_label
A character value used to describe how males are encoded in the
sexcolumn of the dataframe used indata. This MUST match the value for male data in thesexcolumn, and it must be consistent across data sheets. Defaults to"Male".- female_label
A character value used to describe how females are encoded in the
sexcolumn of the dataframe used indata. This MUST match the value for female data in thesexcolumn, and it must be consistent across data sheets. This must be consistent in all data sheets. Defaults to"Female".- left_sex
A character value ("Female" or "Male") describing the sex that will appear on the left side of a faceted plot. Only applies if
facet_by_sexis"yes".- test_type
A character (must be
"wilcox.test","t.test"or"none") describing the statistical model used to create a significance bracket comparing the pre- and post-hormone groups.- y_variable_signif_brackets
A character value. You should only use this if your data did not pass assumptions and you had to transform it.
y_variable_signif_bracketsshould be the name of the column ofdatawhich has the transformed data (e.g. log-transformed data). Raw data will be plotted, but the significance brackets (and t-test/wilcox test) will use the transformed data. If you did not transform the data, this will default to the raw data column.- map_signif_level_values
A
TRUE/FALSEvalue or a list of character values for mapping p-values. IfTRUE, p-values will be mapped with asterisks (e.g. \* for p < 0.05, for p < 0.01). IfFALSE, raw p-values will display. You can also insert a list of custom mappings or a function. For example, usemap_signif_level_values = function(p) if (p < 0.1) {round(p, 3)} else {"ns"}to only display the p-values when they are below 0.1.- geom_signif_family
A character value describing the font family used for the p-value annotations used by
ggsignif::geom_signif(). Defaults to""(empty value, will be replaced with default system font), but can be replaced with a named font. Use a package likeextrafontto load system fonts into R.- geom_signif_text_size
A numeric value describing the size of the text annotations (significance stars or p-values) on the plot. Defaults to
8.- large_axis_text
A character (
"yes"or"no"). If"yes", a ggplot theme layer will be applied which increases the axis text.- geom_signif_size
A numeric value describing the size of the
geom_signifbracket size. Defaults to0.4, which is a good thickness for most applications.- mean_line_thickness
A numeric value describing the thickness of the line used to indicate the mean for a group. Defaults to
1.2.- mean_point_size
A numeric value describing the size of the points used to indicate the means. Defaults to
2.5.- treatment_colour_theme
A dataframe containing treatment names and their associated colours as hex values. See sample_treatment_names_and_colours for an example of what this dataframe should look like.
- theme_options
A dataframe containing theme options. See sample_theme_options for an example of what this dataframe should look like.
- save_plot_png
A character (
"yes"or"no"). If"yes", the plot will be saved as a .png using ggsave. The filepath depends on the current type, but they will all go in subfolders belowFigures/in your project directory.- filename_suffix
Optional character value to add a suffix to the filename of the .png file created with this plot. Could be useful if you want to specify anything about the data (for example, to distinguish between recordings produced in MiniAnalysis vs. Clampfit).
- ggplot_theme
The name of a ggplot theme or your custom theme. This will be added as a layer to a ggplot object. The default is
patchclampplotteR_theme(), but other valid entries includetheme_bw(),theme_classic()or the name of a custom ggplot theme stored as an object.
Value
A ggplot object. If save_plot_png == "yes", it will also generate
a .png file exported to Figures/Evoked-currents/Variance-plots. The plot
will be named in the form of
"Variance-comparison-category-plot_category-plot_treatment-variance_measure.png".
An example filename is "Variance-comparison-category-2-Control-cv.png".
Details
If you specify a test_type, the function will perform a paired t-test or
paired wilcox test and add brackets with significance stars through
ggsignif::geom_signif().
This allows you to visually determine if a change in synaptic plasticity is due to a pre- or post-synaptic mechanism. For more information, please see Huijstee & Kessels (2020).
See also
make_variance_data() to make the data required to make this plot.
Examples
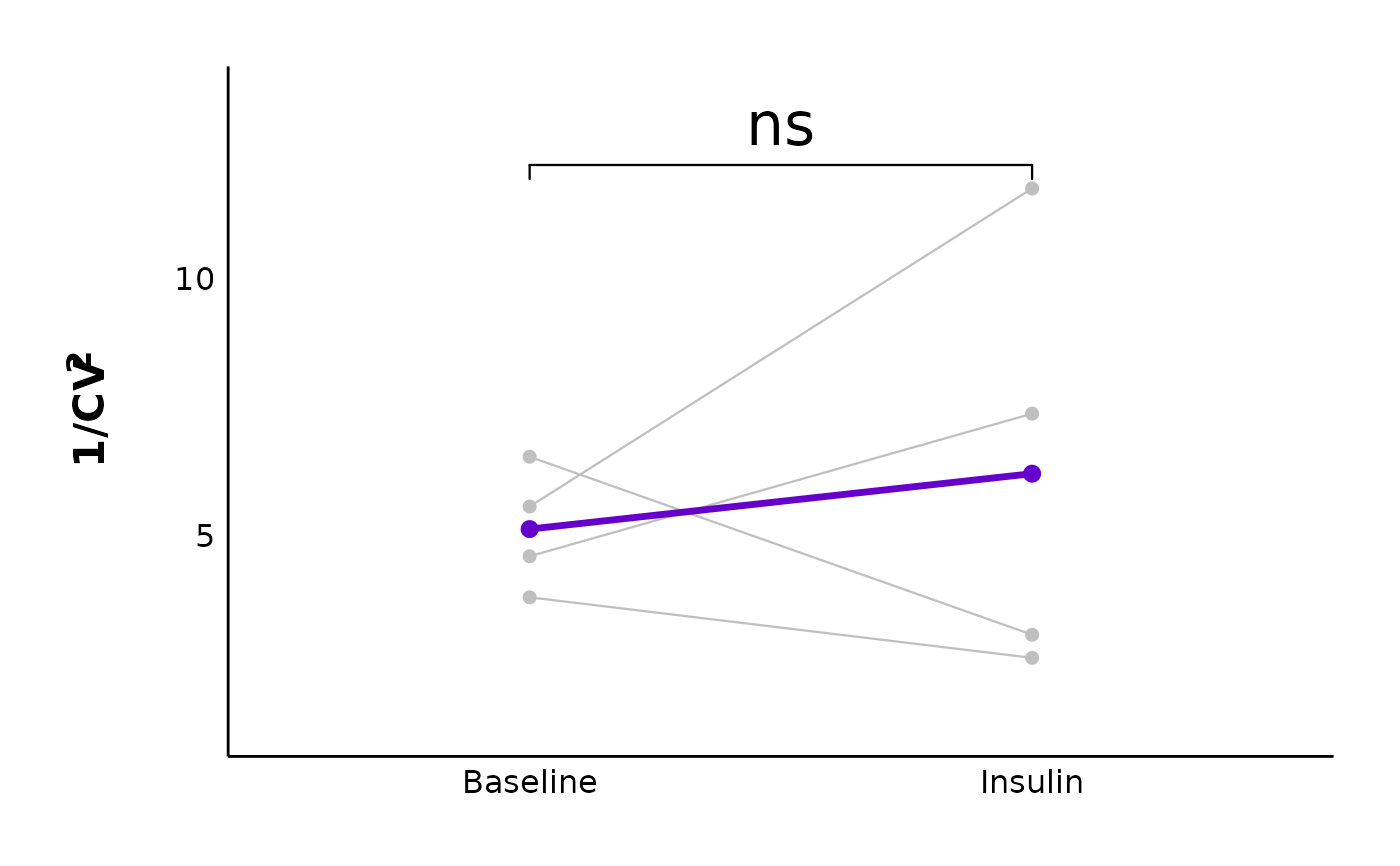
# Without facets
plot_variance_comparison_data(
data = sample_eEPSC_variance_df,
plot_category = 2,
plot_treatment = "Control",
variance_measure = "cv",
baseline_interval = "t0to5",
post_hormone_interval = "t20to25",
included_sexes = "both",
facet_by_sex = "no",
post_hormone_label = "Insulin",
test_type = "wilcox.test",
large_axis_text = "no",
treatment_colour_theme = sample_treatment_names_and_colours,
theme_options = sample_theme_options
)
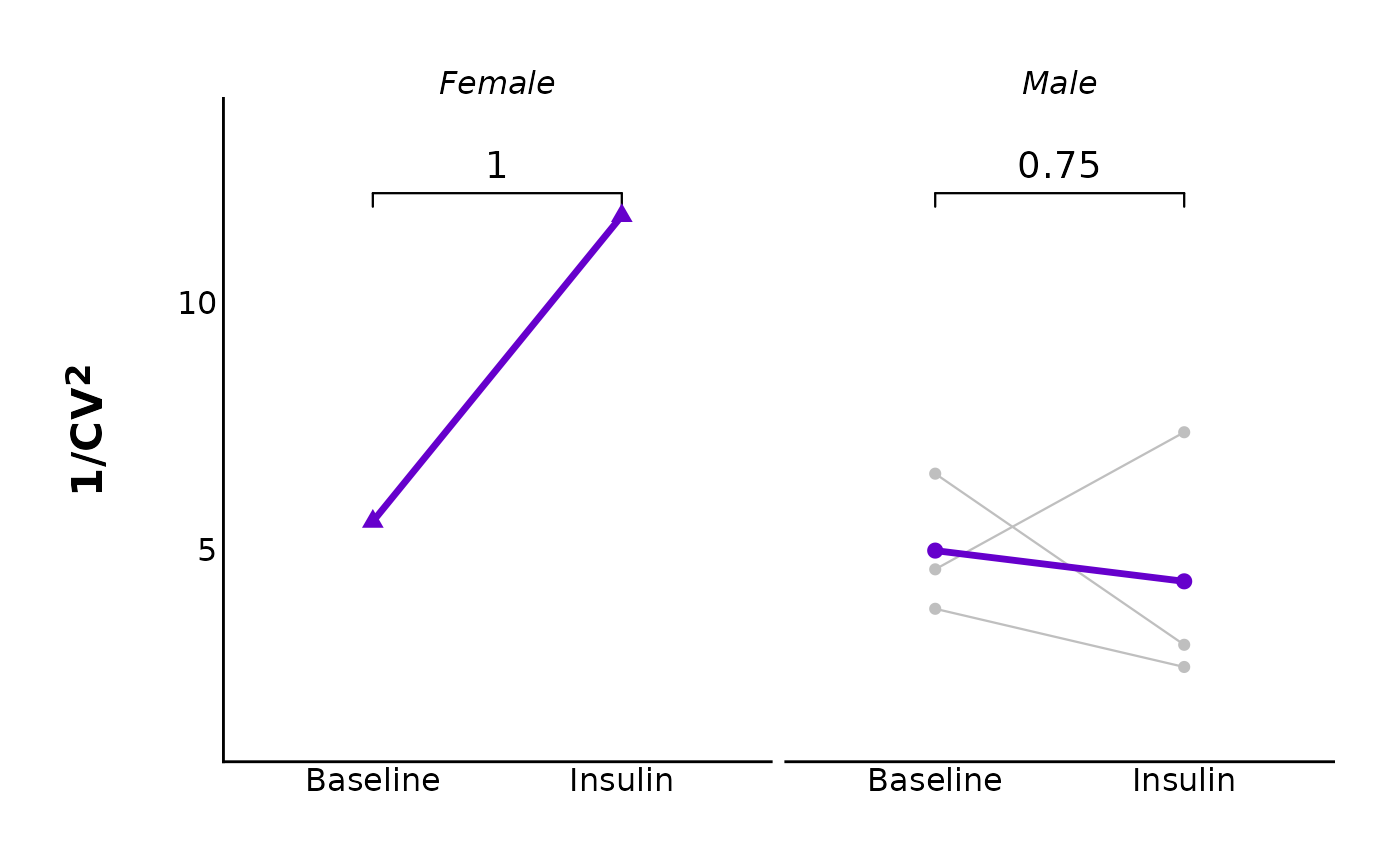
 # With facets
plot_variance_comparison_data(
data = sample_eEPSC_variance_df,
plot_category = 2,
plot_treatment = "Control",
variance_measure = "cv",
baseline_interval = "t0to5",
post_hormone_interval = "t20to25",
included_sexes = "both",
facet_by_sex = "yes",
post_hormone_label = "Insulin",
test_type = "wilcox.test",
large_axis_text = "no",
treatment_colour_theme = sample_treatment_names_and_colours,
theme_options = sample_theme_options
)
# With facets
plot_variance_comparison_data(
data = sample_eEPSC_variance_df,
plot_category = 2,
plot_treatment = "Control",
variance_measure = "cv",
baseline_interval = "t0to5",
post_hormone_interval = "t20to25",
included_sexes = "both",
facet_by_sex = "yes",
post_hormone_label = "Insulin",
test_type = "wilcox.test",
large_axis_text = "no",
treatment_colour_theme = sample_treatment_names_and_colours,
theme_options = sample_theme_options
)